Purple Bitcoin 2023: Bitcoin Purple BTCP is a decentralized currency, created with the aim of preserving a high value without suffering the harmful effects of inflation and uncontrolled issuance, its scarcity and difficulty of obtaining combined with the speed of transactions guarantee a safe and reliable way of storing large amounts of value in a few fractions. Providing freedom anywhere in the world.

Purple Bitcoin
A global freedom for all, fully decentralized currency, created to be a means of free transactions and without central command. Bitcoin Purple is a SHA-256 coin, created and designed similarly to Bitcoin (BTC) but with faster transactions.
BitcoinPurple is made by dozens of people around the world, with the aim of bringing freedom and maintaining stores of value. It is only possible to mine one BTCP per Block, it is possible to mine only 1 000 000.
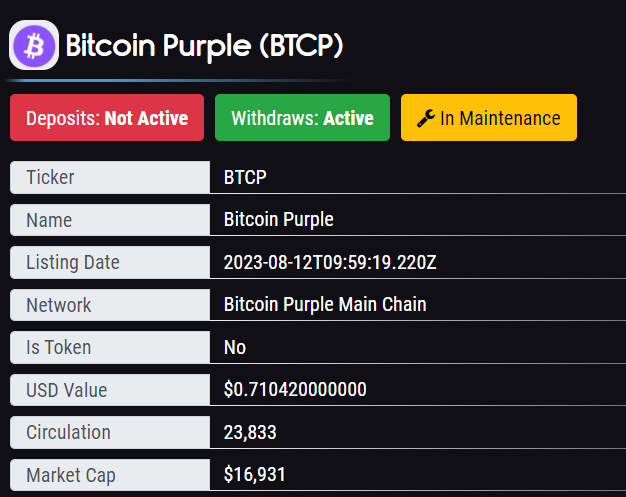
Bitcoin Purple [BTCP] is a cryptocurrency with its own blockchain. The actual price for one Bitcoin Purple [BTCP] is $0.710906. Bitcoin Purple is listed on 1 exchange with a sum of 1 active market. The 24h volume of [BTCP] is $1 097.65, while the Bitcoin Purple market cap is $0 which ranks it as #4116 of all cryptocurrencies.
Purple Bitcoin Coins Unique
A cryptocurrency is fungible by design, meaning every unit is exactly the same and replaceable with another. For example, there’s no difference between one BTC you own and one BTC that another person owns. Colored coins refer to methods that enable adding new elements to fungible coins.
When elements are added to a set of coins, it’s known as coloring those coins because they’re now different from the rest. They have special properties that make them unique and valuable independent of their face value as cryptocurrency.
Purple Bitcoin Coins Work
A Purple Bitcoin coin is a cryptocurrency that includes a promise by an asset issuer to provide a good or service for the owner of the coin. The asset issuer creates colored coins by encoding some of their own cryptocurrency with metadata using a special crypto wallet that knows how to color coins.
The metadata specifies the obligations of the asset issuer to the coin holders. For example, a musician can issue colored coins giving owners the right to attend a concert at a specific date and location. Everyone who has one of the colored coins can then attend.
After creating colored coins, the asset issuer can transfer them to other parties. The transfers are processed as transactions on the cryptocurrency’s blockchain network so they offer the same level of security and irreversibility.
Use cases for Purple Bitcoin Coins
There are many potential use cases for colored coins. Here are a few examples of what can be done with them:
- A company can use colored coins to represent shares, allowing coin holders to trade shares, vote, and earn dividends.
- A community can create its own community cryptocurrency that’s secured by the Bitcoin blockchain.
Subscription services can use colored coins to represent memberships. For example, a streaming company can tie membership to colored coins, making them transferable and secure.
Colored coins can also serve as ownership records for both real-world and digital assets on the blockchain. A colored coin can be used to manage ownership of a painting, image, or e-book, to name a few examples.
Invest In Purple Bitcoin coins
You can’t invest in colored coins since they’re simply a capability of certain blockchains. However, you can invest in cryptocurrencies that have technology related to colored coins.

The best place to start is with smart contract blockchains. Practically anything can be written as a smart contract, so the technology has the same capabilities as colored coins — and much more. If you want to invest in something similar to colored coins, blockchain networks with smart contract functionality are the closest option.
Ethereum was the first smart contract blockchain. It’s also the largest by a wide margin. Here are a few other smart contract blockchains to consider:
You could also try investing in NFTs, although their value is highly speculative. Each NFT has a record of ownership for a specific digital asset, so they also have some similarities to colored coins. There are several NFT marketplaces you can use to buy and sell NFTs, with OpenSea being the largest.
Future Of Purple Bitcoin Coins
Colored coins were a big step forward for blockchain technology. The technology was originally used solely for transferring digital currencies on a decentralized network. Colored coins introduced the idea of storing and transferring more than just money on the blockchain.
As blockchains become more integrated with the real world, we’ll likely see more examples of real-world and digital assets being managed using crypto tokens. Even if this is done using smart contracts, it all comes from the idea of colored coins.
Use Cases For Purple Bitcoin Coins
Colored coins were proposed for a wide range of industries, from gaming to finance, and implemented to a certain extent. They enabled the tokenization of assets on the blockchain, making it easier to trade and transfer ownership. Colored coins also opened up new possibilities for decentralized finance (DeFi) and helped in some ways to bridge the gap between traditional finance and the blockchain.
Given that colored coins enabled asset tokenization, colored coins were largely used for the following:

Asset Representation: Colored coins could be used to represent real-world assets digitally. For example, one could create tokens via colored coins that prove ownership of physical assets like real estate, commodities, or even art.
Tokenized Securities: Colored coins could be utilized to tokenize traditional securities such as stocks, bonds, or company shares. This enabled easier and more efficient transfer and trading of these assets.
Loyalty Programs: Companies could issue colored coins as digital tokens to create loyalty programs. These tokens could be distributed to customers as rewards and can be redeemed for discounts, special offers, or exclusive products or services.
Collecting Virtual Assets: Colored coins were used in online gaming platforms to represent virtual assets, such as in-game items, characters, currency, or on other platforms in the form of collectibles (much like the trading cards initially seen on Counterparty). This allowed players to sell, own, trade, and manage these assets securely.
Intellectual Property Rights: Colored coins could be used to represent ownership or licensing rights for digital content, such as music, videos, or eBooks. This would enable creators to distribute and monetize their work while ensuring ownership is properly recorded.
Colored Coins
Colored coins offer some very interesting features, but they haven’t really caught on, and aren’t being used widely. One reason for this is the creation of the Ethereum blockchain and the fairly mass adoption of ERC-20 tokens. The best use case so far for colored coins has been in creating an ICO. An ICO can be done using colored coins in minutes and with little cost.
Unfortunately, we haven’t seen many businesses spring up to take advantage of this ease-of-use case. In fact, the leading colored coins wallet and service, Coinprism, shut down at the beginning of April 2018. Colored coins were created as a way to issue and transfer assets on the Bitcoin blockchain. A colored coin can be issued to represent anything at all, including stocks, bonds, commodities, real estate, fiat currencies, and even other cryptocurrencies.

Сolored Coin Wallet
Colored coins can be handled through wallets in the same manner as Bitcoin monetary resources can be managed through Bitcoin wallets. Wallets are used to manage the addresses associated with each pair of keys of a Bitcoin user, as well as the transactions associated with their set of addresses. Rather than dealing with cryptocurrencies, colored coin wallets add a layer of abstraction, managing digital assets, such as stocks, and altcoins, which are created on the Blockchain, intellectual property, and other resources.
Potential Of Colored Coins
Making a Bitcoin transaction can be as simple as sending an SMS or email, transferring value directly in a peer-to-peer fashion, without the need for any third-party intermediary. And since colored coins are a type of Bitcoin, this is true when discussing colored coins as well.
This should begin to give you some idea of the potential that colored coins hold. It is quite literally impossible to imagine the tidal wave of innovation and economic growth that such an egalitarian system of capital formation would unleash.
Colored Coins Risks
It’s unrealistic to think that there won’t be some risks to colored coins. While they are part of the Bitcoin blockchain, they are quite different from ordinary Bitcoin, since they represent real-world physical assets and financial obligations. This means every colored coin needs to be issued by an individual or organization, which adds a layer of risk.
The possibility will always exist that the issuer of the colored coin will fail to honor the obligation inherent in the coin. There is even the risk that they don’t represent anything real at all, and are completely fraudulent.

Colored Coins Work
Bitcoin transaction that has been customized by adding metadata. Within Bitcoin’s structure, the ColoredCoin framework allows adding information to a transaction and differentiating one coin from the rest. A coin customized by adding metadata can represent a real-world asset.”
Even though it was only designed to be a cryptography-based currency/collectible, Bitcoin’s scripting language came with the ability to store small amounts of metadata on the blockchain. Initial developers of Colored Coins realized that this data could represent or segregate a particular set of coins. By that, they meant that Colored Coins could be virtual bridges to a real asset, thereby allowing for asset manipulation.
In theory, Colored Coins could be used to represent
- Property
- Stock
- Commodities
- Bonds
- Contract
- Or any other type of asset that needs a Virtual representative
Pros And Cons Of Colored Coins
Now, like everything in the world of technology, colored coins have their benefits and risks.
Pros
- Possibility of being used to represent in a tokenized way what is desired.
- As they are running on the Bitcoin blockchain, they enjoy the strongest, safest, decentralized blockchain network in the world, and with global reach.
- They allow the creation of exchangeable token systems. This property allows for example: to create decentralized exchanges or to carry out atomic exchanges between different colored coins.

Cons
- Highly complex to implement and develop. The appearance of the protocols and other tools for their development improved this situation, but even so, colored coins are more complex to create than other options such as Ethereum’s ERC-20 tokens.
- They put more pressure on the blockchain. The creation of colored coins increases the size of the transactions and this impairs the ability of the network to process transactions. All of this leads to a decrease in the number of transactions that can be processed, drives up the cost of mining commissions, and dramatically increases the size of the blockchain.
- Disincentives miners due to low commissions for colored coins. This is a situation that can lead to a loss of computing power to the network due to low profits for miners, who will then prefer to mine for more profitable cryptocurrencies.
- The fact that some colored coins represent securities or other types of assets related to third parties represents a risk. The fact that a third party represents the interests of a colored coin leads to it being able to simply scam those who participate in said system.
The Benefits Of Colored Coins
Colored coins helped introduce blockchain technology’s uses beyond peer-to-peer (P2P) payments and alternative investments. Here are some other benefits of colored coins:
Expand the use cases of cryptocurrency: Colored coins helped generate excitement about the limitless possibilities of blockchain technology. Not only did these coins give developers greater flexibility, but they also gave non-crypto-related firms, companies, and institutions a potential reason to use crypto in their business strategies, enabling them to increase the adoption of blockchain technology.
Support the security, longevity, and global reach of the Bitcoin blockchain: Although colored coins exist on other blockchains, most use the Bitcoin Network. As the largest and oldest cryptocurrency, Bitcoin has the highest reputation for security, allowing developers to instantly reap the advantages of the global BTC blockchain.
Offer enhanced transparency to issuers: Colored coins allow companies, institutions, or nonprofit organizations to maintain transparency in their internal systems. Since all transactions are verifiable on a public blockchain, it’s easy to verify which wallets hold these coins and where they’re being transferred.
Facilitate wide user reach: While it’s not as simple to create a colored coin versus an NFT, developers with coding experience can use this technology. Portals like GitHub offer plenty of open-source data on colored coins.

Drawbacks To Colored Coins
Colored coins have unleashed a wealth of opportunities for blockchain developers, but there have been a few negative features associated with these cryptocurrencies. Also, as new blockchain technologies gain prominence, colored coins have lost some appeal. Here are some of the most prominent disadvantages of colored coins:
The higher learning curve to create and use: Although anyone can create colored coins, it’s more challenging to use this technology without prior coding experience. There are also fewer services available to make colored coins than minting NFTs.
Declined popularity due to NFTs: Many involved in crypto have shifted their focus to NFTs as they are more accessible in today’s market and offer greater ease and flexibility to developers than colored coins.
Potential legal challenges for coins that track securities: If colored coins are associated with third-party assets like stocks or bonds, they may fall under the jurisdiction of government institutions, which may cause significant legal and tax implications. The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission already oversees security tokens on smart contract blockchains.
Lack of incentives for miners: Since most colored tokens are insignificant in terms of fiat currency, sending them won’t generate high fees on proof-of-work (PoW) blockchains like Bitcoin. Due to these low fees, crypto miners likely won’t prioritize colored coin transactions, which can lead to increased congestion and slow throughput for those using colored coins.
Bitcoin Mining
Bitcoin mining, in and of itself, is not harmful and involves using a computer to solve difficult mathematical equations for the user to earn Bitcoin. The user earns bitcoin by verifying transactions on the blockchain, which is a digital ledger—similar to a bankbook—that keeps track of all the transactions of a given cryptocurrency. Each time a hash is solved, the user who solves it earns Bitcoin.
However, to solve math problems, a computer has to run nonstop, expending a lot of central processing unit (CPU) power. This takes a lot of electricity. Hackers have begun hijacking other people’s computers to use them, their resources, and the user’s electricity to mine Bitcoin, which the hacker can then cash in on.

Bitcoin Mining Work
Bitcoin mining uses malware. Hackers have written malware with the ability to access your computer and use its resources to mine Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. For the hacker to earn cryptocurrencies, they have to verify transactions on a blockchain. Cryptocurrencies depend on this to maintain solvency.
Each transaction generates an ID labeled with a hash. On the Bitcoin blockchain, a hash is a 256-bit encryption, which is essentially a password. Each computer on the network tries to figure out the 256-bit password, and if it gets even one character wrong, the hash is not solved. Other computers work to verify the authenticity of the solutions the “winning” computer came up with.
All of this work is rewarded with cryptocurrencies—in this case, bitcoin. In some cryptocurrency ecosystems, users also get voting rights in the system’s governance structure. This means they get to cast a vote regarding the decisions the development team makes about the future of the currency, its token, and how it will be used.
Bitcoin Mining Risks/Security Risks
If your computer is hacked and bitcoin mining malware is installed, your computer may be destroyed and your electricity bill may skyrocket. Because Bitcoin transactions require so much computing power to verify, the hardware for Bitcoin mining has to be cooled constantly by special fans. Your average cell phone, desktop, or laptop computer does not have the cooling capabilities to keep the CPU from overheating.
As a result, when a computer is hijacked for cryptocurrency mining, it often overheats and burns up. Also, 100% of your device’s computing power may be used for mining. This can bring your computer’s operation to a halt when it comes to business-critical computations. Bitcoin mining software is designed to consume huge portions of a computer’s processing power, leaving little to no room for even relatively low-demand tasks.
In addition, your computer could be used as a launching point to spread the malware to other computers that connect to your network. This could erode the trust you have with customers, business partners, and others who depend on you to deliver services and communications safely. However, there are also specific types of scams that hackers use, and each of these can be a threat to users on your network.

Wallet Scams
Bitcoins are held in Bitcoin wallets. With a wallet scam, fake wallets are set up online, and scammers will request that you either give them money upfront or they will provide you with a Bitcoin address that ends up putting your funds in their wallet, not yours. There are also fake hardware wallets with built-in vulnerabilities that make it easy for scammers to get in and steal your bitcoins.
Mining Scams
Some companies pretend to provide mining services using a Bitcoin mining cloud. They take your money but never mine any Bitcoin for you. People often fall for the scam because they want to get their hands on the Bitcoin cryptocurrency, and while there are legitimate services out there, some are fraudulent.
Exchange Scams
When you trade bitcoin, especially for another digital currency, you may use an exchange. Each transaction requires a fee. Scam exchanges may lure in unsuspecting bitcoin holders with very low fees. But they then steal your money by using the wallet ID and password you provide.
Secure Your Devices from the Risks
If you fail to secure your devices against these kinds of attacks, your device, as well as others connected to the networks it uses, can become infected and suffer from failure. The CPU may get too hot, and the device could literally melt or burn up. In addition, the vast majority—as much as 100%—of the device’s computing power can be hijacked. This could make it useless for the user, stopping business and creating a time-consuming task for the IT team charged with eradicating the threat.
Avoid Public Wi-Fi Networks
Public Wi-Fi networks are a popular target for those who want to mine cryptocurrency on the Bitcoin blockchain using other people’s devices. Because the connections are not secure, it is relatively easy for a hacker to gain access to a user’s computer and install malware in a public network. Avoid connecting to the internet using a publicly provided connection like in a café or store.

Use a VPN
A virtual private network (VPN) can offer adequate protection against cryptojackers. With a VPN, you can access a network that is separate from other users. In this way, only you and other people with a username and password can gain access. Also, traffic on a VPN is encrypted, making it far harder to hack than traditional network activity. This can prevent cryptojacking on your device.
Secure Your Devices
To secure your devices, the following measures should be implemented:
Antivirus protection: Antivirus protection programs filter threats, like mining botnet infections, and keep them from attacking your devices. They can also quarantine and eliminate threats that have already penetrated your device, freeing your computer from its effects.
Use a personal VPN: On each device you use, you can access the internet with your own personal VPN. This keeps your internet use private and secure.
Use a firewall: If your internet activity happens behind the protection of a firewall, threats like those stemming from Bitcoin crypto mining hacks can be kept out. Also, because the firewall can monitor the data leaving your computer, it can prevent your device from being used to hack into others.
Purple Bitcoin 2023, Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How long has Bitcoin Purple been trading?
Bitcoin Purple has been trading for 53 months (4 years) now. According to our records, it started trading on Friday, September 1st, 2023, for a first price of $105.71.
How volatile has Bitcoin Purple been over the last 30 days?
Bitcoin Purple’s 30-day volatility has been 174.39%.
How volatile has Bitcoin Purple been over the past week?
Bitcoin Purple’s 7-day volatility has been 84.24%.
What was the highest Bitcoin Purple price in USD?
Bitcoin Purple’s all-time high was $1.72. Right now, Bitcoin Purple is priced at $0.7103, 58.61% lower than its all-time high.
What was Bitcoin Purple’s highest price in BTC?
Bitcoin Purple’s all-time high in BTC was 0.01141850. Right now, Bitcoin Purple is priced at 0.00002705, % than its all-time high.
What was Bitcoin Purple’s growth rate over the last 3, 6, and 12 months?
Bitcoin Purple’s price ranged between $2.32 and $0.3417 over the past 3 months, which means it had a compound monthly growth rate of -47.20%, and an extrapolated compound annual growth rate of -1.00%.
What is Bitcoin Purple’s cumulative return since the day it first started trading?
Bitcoin Purple has dropped 99.52% since it first started trading.
How many winning months has Bitcoin Purple had since its first trading day?
Bitcoin Purple had about 58.00% winning months of its total trading age of 53 months.