5 blockchain uses in digital finance: There are a number of key areas where companies can use blockchain in financial software and systems. While banks are reluctant to openly discuss potential uses of blockchain, a number of them have recently commissioned studies to identify exactly where they can. These include Citibank, Credit Suisse, and the World Economic Forum.

Plan well when you build blockchain financial services applications:-
How can you successfully build and implement blockchain financial services applications?
5 blockchain uses in digital finance: Choose between a public and private blockchain. You will only want to allow only trusted parties to join your network, moreover, you will need to implement access control to protect sensitive data. You also need to implement scalability and the best performance, therefore, public blockchains might not work for you. As we outlined in “Public vs private (permissioned) blockchain comparison”, you will likely need to use an enterprise blockchain.
Find an appropriate hosting provider for your blockchain network.

Smart Contracts on Blockchain:-
5 blockchain uses in digital finance: Arguably the most impactful application of blockchain in finance is its ability to efficiently establish trust through smart contracts.
Smart contracts are similar to physical contracts, except the stipulations of the contract are fulfilled in real time via the blockchain. Smart contracts are beneficial, especially to the finance sector, for numerous reasons. These contracts are fulfilled instantly after all stipulations are met, do not require any middlemen and add heightened levels of security.
Smart contract technology is currently at the top of almost everyone’s needs because of its efficiency and privacy. Here are four companies instituting blockchain-based smart contracts in an effort to get ahead of the curve.

Blockchain Examples for Financial Use Cases:
Payments
5 blockchain uses in digital finance: Blockchain technology using digital currency could be used in both domestic and international fund transfers. While on the domestic front banks are likely to resist implementing blockchain solutions, given that they have already invested heavily in existing centralized solutions, internationally they stand to benefit enormously from such a change.
Inadequate infrastructure also presents a security concern for many transfers since these systems are more open to cyber-attacks and data breaches. These attacks could disrupt transfers and even redirect the funds to a third-party account.

Remittances
The figures relating to how much of certain developing countries’ entire GDP is down to remittances are quite an eye-opener. Haiti has one of the world’s highest remittances vs. GDP rates, some 29% of its entire GDP.
Traditionally, the remittance market has been dominated by MTO-model companies such as Western Union. Though banks do actually offer this service, the inherent problems of cross-border remittances, such as creating safe and secure partners where receivers can collect their money, have made many banks wary of the market.
Payment gateway
5 blockchain uses in digital finance: Next in the list of blockchain examples for finance industry solutions is a payment gateway. A recent successful ICO by startup Mycelium brought attention to how blockchain could be used to facilitate next-generation payment systems. The company’s goal is to “bring merchants and consumers together with a blockchain card and mobile wallet.”
While the concept of cryptocurrency existed long before Mycelium, the company’s decision to use digital tokens as a way to facilitate the transfer of wealth, as well as to incorporate a payment gateway facility, generated huge interest in its ICO.
Mycelium’s business model makes the need for traditional bank payment processing redundant.

Trade Finance
Trade finance is the last of blockchain examples in our list. The automation of transactions essential to trade finance will help the financial services industry make huge savings after blockchain solutions are introduced.
The use of smart contracts to automate approval workflows and clearing calculations will help reduce processing times and enable banks to massively reduce the number of employees needed for this task too.
While this is not good news for their staff, it will also benefit the banks by helping to reduce the number of errors resulting from human mistakes.
Improving keeping record
The global finance industry holds trillions of bank records that relate to everything from personal account data to stock market transaction ledgers that record stock purchases. A huge majority of these transactions could be recorded using blockchain digital ledgers which would be unalterable and so prevent fraud.
Not only that, but the decentralized nature of the transactions would also give banks better security over the records. Since the other parties involved in the transaction also receive a record, disputes over such things as missing or incorrect transactions would be a thing of the past.

Identity
Blockchain could help banks finally overcome a problem that has been troubling them for years. Banks are responsible for verifying their customer‘s identities. These rules exist in nearly every country in the world and aim to help prevent fraud and money laundering.
The cryptographic protection offered by blockchain, which requires a secure key to access, would ensure that all parties involved in a transaction would be clearly known to the ledger. Since identification is required by law, this feature is essential to all financial transactions.
Blockchain Payment Processing
5 blockchain uses in digital finance: One of the most attractive applications of blockchain in fintech is its ability to process payments almost instantaneously and in a manner that protects data integrity.
Because the basis of DLT is to bypass centralized institutions, moving money from peer-to-peer is as simple as pressing a “send” button on a phone. Once initiated, the nodes in the blockchain work to unanimously accept or deny the payment in an instant. There’s no need for cash to sit in limbo for days while the bank processes the transaction, nor is it burdened by exorbitant fees.
By conducting money transfers with blockchain, both customers and banks could save an unprecedented amount of time and money. Blockchain-based currencies are also universal, meaning there are no exchange rates, international transfer fees or confusing country-by-country laws that prohibit the transfer of cryptos.
By conducting money transfers with blockchain, both customers and banks could save an unprecedented amount of time and money. Blockchain-based currencies are also universal, meaning there are no exchange rates, international transfer fees or confusing country-by-country laws that prohibit the transfer of cryptos.
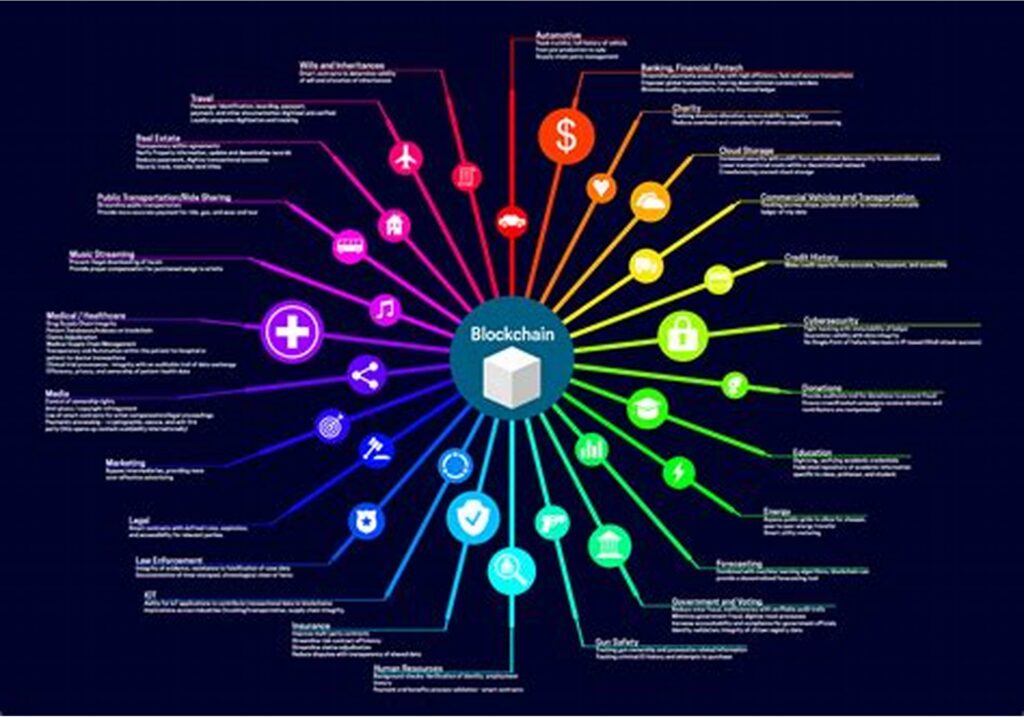
What are the Blockchain Use Cases in Financial Services?
- Capital Markets Issuance Sales and trading …
- Asset Management Fund Launch Cap table management …
- Payments and remittances Domestic retail payments Domestic wholesale and securities settlement …
- Banking and Lending Credit prediction and credit scoring Loan syndication, underwriting and disbursement …
- Trade Finance Letters of credit and bill of lading Financing structures
- Insurance Claims processing and disbursement …

What are the top 5 blockchain examples in financial services:–
The top 5 blockchain examples in financial services are as follows:
Payments: Banks and financial services institutions can expedite payment transactions using blockchain.
Remittances: Blockchain can expedite international fund transfers, and companies like Abra and Bit Pesa are already using it.
Payment gateway: A blockchain platform can help banks and financial services institutions to implement a payment gateway facility easily.
Trade finance: Blockchain smart contracts can streamline workflows and expedite trade financing processes.
Record keeping: The immutable and distributed ledger technology of blockchain improves record-keeping and data-sharing processes, which can transform clearance and settlement processes in financial services institutions.

Which banks and financial services institutions are using/exploring blockchain:-
The following are examples of banks and financial services institutions that are using/exploring blockchain:
Banco Santander.
Barclays.
UBS, the Swiss investment bank.
Citibank.
Deutsche Bank.
Commonwealth Bank of Australia.
DBS Bank.
Which enterprise blockchain frameworks are popular in the banking and financial services sector:
5 blockchain uses in digital finance: The following enterprise blockchain frameworks are popular in the banking and financial services sector:
Hyperledger Fabric.
R3 Corda.
Quorum from JP Morgan.
HOW CAN BLOCKCHAIN REVOLUTIONIZE THE FINANCE SECTOR:-
5 blockchain uses in digital finance: The financial services industry is estimated to reach USD 2.6 Trillion by 2022. The global financial system deals with trillions of dollars a day and serves billions of individuals. With such great heights come many challenges that the finance industry has been facing for a long time.
Ranging from the high cost of multiple stakeholders to delays, excessive paperwork, and data breaches, these challenges have been the root cause of massive amounts of losses the industry faces every year. As per a PWC report, 45% of the financial intermediaries like stock exchanges, money transfer services, and payment networks face economic crimes every year. Blockchain technology can be a possible solution to the challenges of the global financial system.
See also” cryptocurrency Shibu Inu coin in 2023″
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain is a network of peers who can interact, communicate, and transfer information without being dependent on a centralized entity. The key features of blockchain include transparency, security, immutability, and decentralization.
What are the Benefits of Blockchain in Finance?
The Ethereum blockchain enables more open, inclusive, and secure business networks, shared operating models, more efficient processes, reduced costs, and new products and services in banking and finance. It enables digital securities to be issued within shorter periods of time, at lower unit costs, with greater levels of customization. Digital financial instruments may thus be tailored to investor demands, decreasing costs for issuers, and reducing counterparty risk.
How does the Digitization of Financial Instruments Impact Finance?
The digitization of financial instruments – comprising digital assets, smart contracts and programmable money – takes the benefits of blockchain further by forging unprecedented levels of connectivity and programmability between products, services, assets and holdings. These digitized instruments will redefine the processes of commercial and financial markets, creating a new paradigm where value is brought at every touch point.
How does blockchain impact capital markets?
Capital markets refers to the pairing of issuers with demand for capital, to investors with corresponding risk and return profiles. Whether issuers be entrepreneurs, startups or large organizations, the process of raising capital can be challenging. Firms face increasingly stringent regulations, longer times to get to market, volatility from interest rates and liquidity risk. Particularly in emerging markets, they must navigate the lack of rigorous monitoring, thorough regulation and sufficient market infrastructure for issuing, settlement, clearing, and trading. Blockchain offers multiple benefits for several capital market use cases:
How does blockchain impact asset management?
Venture capital firms, private equity firms, real estate funds, and specialty markets are facing demands to improve liability risk management, adapt more dynamic decision-making structures, and address the increasing complexity of ever-changing regulations. Blockchain can effectively streamline asset and stakeholder management. It allows.
How does blockchain impact global payments and remittances?
Global payments and remittances today are executed by a number of intermediaries that exact tolls for their service. It takes 2 to 7 days and costs a global average of 6.94% to send $200 between countries. This means that remittances are directly reduced by $48B through fees, intermediaries, and financial institutions. Blockchain can streamline payment and remittance processes, reducing settlement times and significantly reducing costs. It allows.
How does blockchain impact banking and lending?
Core banking comprises of transaction, loan, mortgage, and payment services. Many of these services depend on legacy processes of execution. For example, between information verification, credit scoring, loan processing and distribution of funds— it takes 30 to 60 days for individuals to secure a mortgage, and 60 to 90 days for small or medium enterprises to secure a business loan. Blockchain can streamline banking and lending services, reducing counterparty risk.
How does blockchain impact trade finance?
Trade finance refers to the infrastructure, processes and funding that support international trade supply chains. The industry continues to rely on paper-based processes that are susceptible to security vulnerabilities. Individual transactions can take as long as 90-120 days in order to process letters of credit, verify documents, and establish trust among stakeholders.
How does blockchain impact insurance?
Trade finance refers to the infrastructure, processes and funding that support international trade supply chains. The industry continues to rely on paper-based processes that are susceptible to security vulnerabilities. Individual transactions can take as long as 90-120 days in order to process letters of credit, verify documents, and establish trust among stakeholders. Blockchain can digitize the entire trade finance lifecycle with increased security and efficiency.
How does blockchain facilitate compliance?
Regulatory compliance has become increasingly important in the commerce and finance space. It is necessary in order to ensure that financial institutions respect laws, rules, and regulations applicable to their activities. It is a huge challenge for firms to keep up with the pace and complexity of regulatory change— particularly when firms operate across borders and are thus exposed to multiple regulatory regimes.